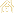Knowledge and skills control in English
1. By the end of the school year students of the first forms are to master skills as following:
a) speaking – 5-7 sentences about the topic;
b) writing – letters, words;
c) reading – sounds, words, sentences, short known texts (on the expressiveness of reading).
2. By the end of the year students of the second forms are supposed to:
a) know all vocabulary for the second form;
b) relate topics (7-8 sentences) (the quantity of topics during a year – 5-6, depending on preparedness of students);
c) read a text aloud.
3. By the end of the school year students of the third forms are supposed to:
a) know all vocabulary for the third form (words, irregular verbs);
b) relate topics and answer the questions about the topic (during a year at least 6 topics must be learned);
c) read and retell an unknown text within a program.
4. Students of the fourth forms in the first-third quarters sit for the test:
a) the first stage – words, irregular verbs, preposition combinations (a separate mark is put for each type of control, and then all the marks are added and the middle arithmetical for the vocabulary is derived. After telling a topic and answering the questions the marks for these two types of control are added up to the mark for vocabulary and are divided by 3 forming in this way a mark for the oral speech) (these requirements of vocabulary are the same for students of all forms and won’t further be deciphered);
b) a word dictation (new vocabulary) – 24 words;
c) the second stage – an oral topic plus three questions on not necessarily concerning a topic (questions are appraised separately; in this way a student gets a separate mark for a topic and a separate mark for answering the questions; these marks are added to the mark for the vocabulary, a received number is divided by three and we get a mark for the oral speech, which is put in the class register); a teacher of a group prepares a list of grammar structures and a list of verb tenses, learned during a particular quarter;
d) in the fourth quarter students write a topic, one of all learned during the year (each sudent gets an individual topic, there should not be fewer than eight of them). Except this they pass the vocabulary (to their teacher) orally and write an annual headmaster's grammar test.
5. Students of the fifth forms sit for the test:
a) in the first quarter – the same, as in the fourth form ( pass to the teacher, who works with this group, not to the examiner; at the end of the first quarter marks are not inserted in the computer);
b) in the second and third quarters:
- the first stage – vocabulary (on the same conditions, as for the fourth form); in writing – a textual dictation (6-7 sentences, approximately 30 words – might be from the texts in a textbook learned during this quarter);
- the second stage – a topic plus three questions, that are not related to the topic (assessment of a topic and questions here and further on is the same, as in the fourth form);
c) in the fourth quarter – vocabulary orally ( to their teacher or, by a teacher’s wish, to a colleague from another group); in writing – five questions to a text after listening to it (the teacher reads a text, and the director of studies prepares it; the text is based upon the learned material) and an annual headmaster’s grammar test.
6. Students of the sixth forms sit for the test:
a) in the first-third quarters:
- the first stage: vocabulary; in writing – 6 questions to translate from Ukrainian into English with words, grammar structures and verb tenses learned in this quarter (the teacher prepares a list of the words, structures and verb tenses for an examiner);
- the second stage: a topic plus three questions;
b) in the fourth quarter; orally: vocabulary; in writing: retelling a listened text and asking five questions to it; an annual headmaster’s grammar test.
7. Students of the seventh forms sit for the test:
a) in the first quarter:
- the first stage: orally: vocabulary; in writing: own sentences with 12 new words;
- the second stage: a topic plus three questions;
b) in the second and third quarters:
- the first stage: vocabulary; in writing: a situation with the use of six words (new vocabulary) which are given by an examiner;
- the second stage: a topic plus three questions;
c) in the fourth quarter:
- orally: vocabulary; in writing: a composition with the use of 12 new words; an annual headmaster’s grammar test.
8. Students of the eighth forms sit for the test:
a) in the first and second quarters:
- the first stage: vocabulary; in writing: to compose a situation on a free topic, using six words from 12 proposed, that are given by an examiner;
- the second stage: a topic plus three questions;
b) in the third quarter:
- the first stage: vocabulary; in writing: to compose a situation on a given topic with the use of six words from 12 proposed;
- the second stage: a topic plus three questions;
c) in the fourth quarter:
- orally: vocabulary; in writing: a composition on a free topic with the obligatory use of vocabulary including phrasal verbs and grammar structures learned during the year.
Criteria of assessment of headmaster’s tests in English
9-th form
1.1. A writing component:
a) 1-3 quarters: the translation of word combinations and sentences, which contain new lexical and grammatical material (8 sentences – vocabulary and 6 sentences – grammar)
1.2. An oral part component:
a) the first quarter – analogous to previous forms. The answer is recorded on tape. The number of sentences is not limited, but there mustn’t be fewer than 24. Afterwards two-three questions follow. The answers to the questions should reflect full mastery of material and preparedness to comment in any statement uttered in the topic.
b) the second and the third quarters – speaking on the given situations. There is one minute given to think over the situation. The situations can be of two types: 1) a general type; for instance: imagine you are a London pigeon that lives in Trafalgar Square. Describe your feelings and life-style. 2) contextual: prove that the modern rubs shoulders against the old comparing London and Kyiv. The quality of answers is analyzed by a particular scheme which is below.
It will be useful to involve the material from other subjects (history, chemistry, physics, biology, Ukrainian literature, world literature and others). The main aim of the "situation" is to determine the ability of arranging blocks of material from various spheres of knowledge. The answer must include not fewer than four certain blocks of material learnt by heart and attached to the given situation, without loosing the logic of narration. The best way of the answer is to transfer fully well learned material to the context of the situation.
10-th form
2.1. A writing component:
a) the first, second and third quarters – writing an essay on the given topic. The requirements of the essay are below. They include a writing retelling the plot of the videotape.
b) the fourth quarter – includes a grammar test and writing an essay.
2.2. An oral part component:
a) the first quarter – work in pairs at a coherent translation. One student answers on the given topic (analogously to the 9-th form, but with the obligatory coverage of the personal vision of the problem). Then his/her partner gives a coherent translation in Ukrainian. Periodicity of a coherent translation is two – three sentences. A total amount of sentences is not confined but not fewer than 24. The criterion of a successful translation is speed, exactness and literacy of the Ukrainian language. Asking for saying again after a clearly expressed idea is considered to be a mistake. After the situation some questions may be asked for more precise definition, which are also obligatory for the translation. Later partners change over their roles. Partners are the students from the same academic group. Pairs are determined by interrogator before work. The situation coverage must have an individual feature with the use of various informational block prepared in advance. Repeating the same coherence of the interpretation of material and a great number (5-6) of sentences, used one after another by several students is regarded as a mechanical memorizing of material and as a mistake.
b) the second quarter – a dialogue between two partners on the given situation by the choice of an interrogator. A conversation between partners on the situation supposes an initiating conversation of both participants (an interrogator chooses partners).
c) the third quarter – a dialogue between two partners on the given situation by the choice of an interrogator. A conversation between partners on the topic supposes an initiating conversation of three participants (an interrogator chooses partners). The conversation is recorded on a videotape.
11-th form
3.1. A writing component:
a) the first and second quarters – writing an essay;
b) the third quarter – test in grammar and vocabulary and writing an essay.
3.2. An oral component:
a) the first and second quarters – discussion in the group on video material.
The assessment of high school students knowledge and skills in English is based on the experience received by the teachers within the introduction of the International Baccalaureate Organization Programme at school.
In the 9th - 11th forms one mark is put for the oral component, and this mark integrates indices by the following scheme:
Essay Writing Requirements
1. An opening paragraph must include a topical sentence.
2. A topical sentence of each paragraph must have a key word of a paragraph.
3. A closing paragraph must include a main rephrased idea with a conclusion about the proof.
4. All paragraphs must include linking words.
5. Students pick out topical sentences, key words & linking words in different colours .
6. An idea is expounded logically & coherently.
7. Grammar & vocabulary must correspond to the level of learned material.